


The Nativity
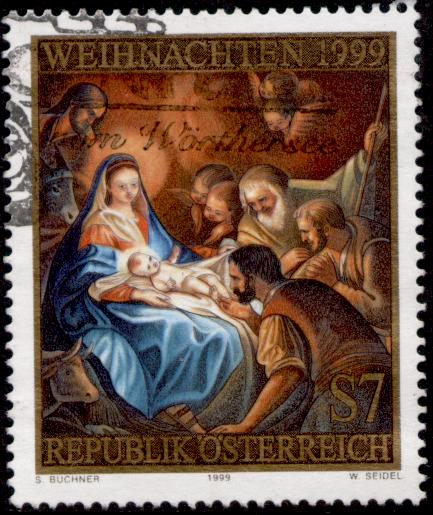
The nativity narratives in the Gospel of Luke and the Gospel of Matthew focus on quite different aspects of the event. The Gospel of Mark, considered the earliest and most historical gospel according to the doctrine of Markan priority, does not include a nativity narrative.
In Luke, Mary learns from an angel that the Holy Spirit has caused her to be with child. Mary points out that she is a virgin and the angel responds that "with God nothing shall be impossible." Shortly thereafter, she and her husband Joseph leave their home in Nazareth to travel about 150 kilometres (90 miles) to Joseph's ancestral home, Bethlehem, in order to register for a census ordered by Emperor Augustus. Finding no room at the inns, they lodge in a stable. There Mary gives birth to Jesus. An angel of the lord goes to the fields and tells the shepherds the "tidings of joy." A heavenly host proclaims, "Glory to God in the highest, and on earth peace to men on whom his favour rests." The shepherds come to the manger to adore the infant Jesus (Luke 1:5-2:20).
In Matthew, magi arrive at the court of King Herod in Jerusalem and ask, "Where is the child who has been born king of the Jews? We have observed the rising of his star, and we have come to pay him homage." (Compare to Numbers 24:17.) The word magi is traditionally translated as "wise men." The word connects them to the magi of Babylon who select Daniel their chief in the Book of Daniel. Daniel's magi interpret dreams and other portents. The book was well-known in ancient times for its prophecy concerning the messiah[10](Daniel 9:24-27), a man who will be sent by God to lead the Jewish people.
Neither the names of the magi nor their number are specified in the Bible, but tradition tells us there were three: Balthassar, Melchior, and Caspar. Balthassar is a Greek version of the Babylonian name Belshazzar. This is the name of a king in Daniel. Melchior means "The king is my light" in Aramaic. Caspar is a Latinized version of Gondophares, a Parthian (i.e. Persian) name. The magi are sometimes called kings because of prophecies that kings will do homage to the messiah (Isaiah 60:3, Psalms 72:11).
Herod is disturbed by the magi's words and questions them closely, attempting to determine when the star first appeared and when the child was born. The king asks his advisors where the messiah will be born. They answer Bethlehem, birthplace of King David, and quote Micah 5:2-4. "When you have found him, bring me word so that I may also go and pay him homage," a deceitful Herod tells the magi.
As they travel to Bethlehem, the magi follow the star of Bethlehem, which leads them to a house where they find Jesus. Jesus is no longer in the manger described by Luke. He is a child (paidion), not an infant (brephos). The magi present Jesus with gold, frankincense, and myrrh. (If these gifts were chosen in view of Isaiah 60:1-7, it may explain the magi's earlier trip to Jerusalem.)[11] In a dream, the magi received a divine warning of Herod's intent to kill the child, who he sees as a rival. Consequently, they return to their own country without telling Herod the result of their mission. An angel tells Joseph to flee with his family to Egypt. Meanwhile, Herod orders that all male children of Bethlehem under the age of 2 be killed. After Herod's death, the family settles in Nazareth (Matthew 2:1-23).
NEXT: Other Dates of Celebration

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|